Features
Add-in Reshape.XL includes
130 basic combinable functions. Using them you can
quickly and easily make very complicated data transformations and processing. Their architecture
and basic definition were strongly inspired by languages SQL and R.
Until now, similar features have been available only for programmers
through the scripting languages. With the Reshape.XL add-in, these
features are accessible also for you inside a simple to use visual
interface. Add-in functions were divided into seven basic groups.
These logical groups form the individual ribbon tabs.
#Reshape
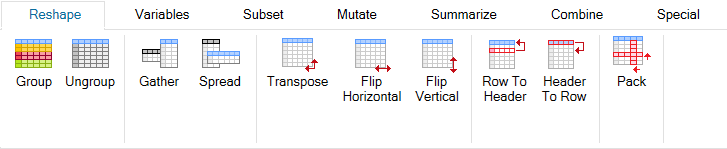
The ribbon tab Reshape contains basic functions for editing the
general character of your datasets. For example, the Group -
Ungroup functions are used to create "virtual sub-tables".
Following functions are performed individually in these sub-tables.
The Gather and Spread functions serve as "Rows to Columns" and
"Columns to Rows" transformations. With Transpose and Flip, you
can rotate your datasets. Pack function allows you to automatically
erase rows and columns that are completely empty.
#Variables
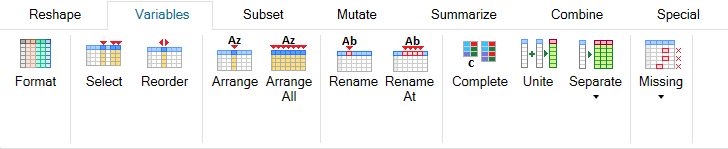
Ribbon tab Variables contains "column-based" functions. For
example, you can format your variables (data type), select them,
reorder, arrange or rename. The Complete function serves to
complete the missing combinations in your dataset (implicit
missing values to explicit). Next, you can combine or divide
the variables. Finally, the described tab includes functions
for working with missing values.
#Subset
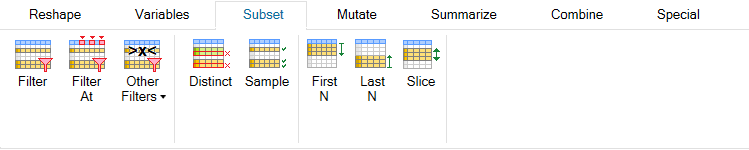
Functions from the Subset group are used to select rows (records)
from your dataset - "row-based" functions. You can filter these
records in multiple ways - you can select unique records, you
can randomly sample your dataset, you can select first or last
N dataset records and finally, you can select dataset records
using the sophisticated Slice function.
#Mutate
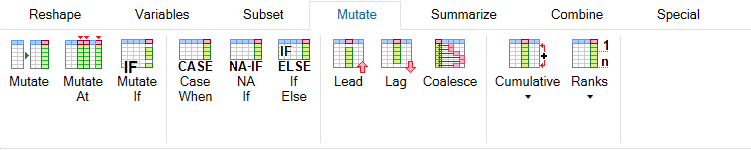
Mutate functions serve to modify existing or create new variables.
You can edit / mutate your variables step by step or several at
once. Here you can find also functions for "conditional editing"
which modify your variables in relation to the defined selection
criteria. Furthermore, you will find a number of other features
that are well known from the SQL language, such as Lead, Lag or
Coalesce commands or cumulative (e.g. Cumulative Mean) and
ranking (e.g. Row Number or Rank) functions.
#Summarize
Another group is focused to summarization. These functions computes
selected statistical values such as minimum, sum, mean, median,
percentile or interquartile range. These functions can be applied
to the entire dataset (all records) or to dataset groups.
#Combine
The following group of features can be used for datasets combining.
The Join function is inspired by a similar function from SQL
language and with different settings you can achieve different
types of joins such as full join, left join, anti-join or outer
join. In addition, you can use other functions that combines
datasets such as Intersect, Except, Set_Diff or Union. Using the
Bind_Cols function, it is possible to insert columns from one
dataset to another one.
#Special
The last group contains a set of specific features. These are
divided by the data type for which are designated. These functions
you can use to process variables in numeric, string and date-time
formats. For example, you can anonymize categories before your
statistical analyses, parse time and date values from specific
formats, or use several advanced string related functions.
Individual add-in functions can be optionally combined. In this way, you can
design and execute very advanced types of data transformations
and adjustment. On the other hand, their definition is extremely
fast, simple and efficient.